Liver Detox Treatment
Navigating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Silent Health Epidemic
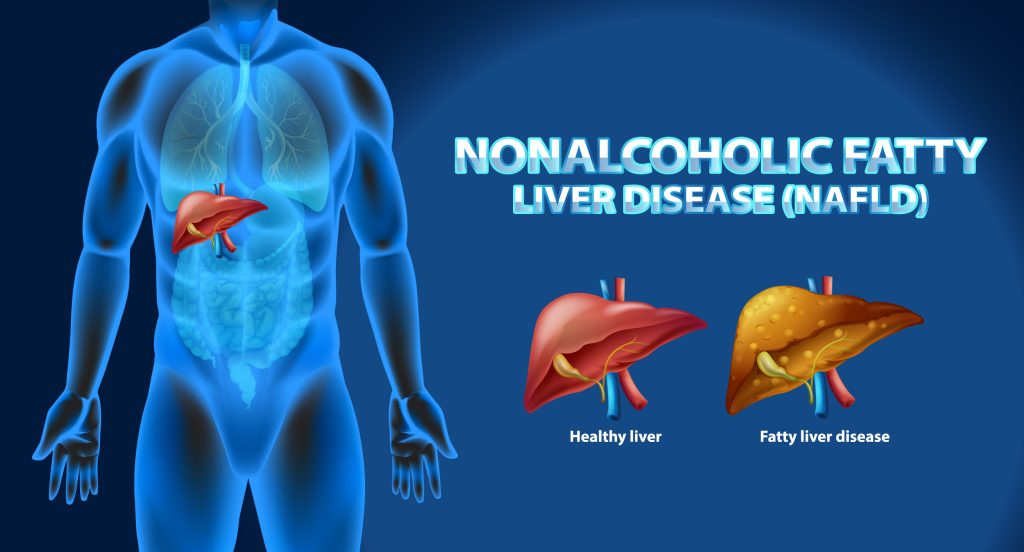
In an era where unhealthy lifestyles and dietary choices have become all too common, a lesser-known but equally concerning health issue has emerged: Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Despite its silent nature, NAFLD has grown to become a significant public health challenge globally. In this article, we explore the intricacies of NAFLD, unravelling its causes, potential complications, and avenues for prevention and management.
Decoding Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
NAFLD is a term encompassing a range of liver conditions marked by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells, resembling the impact of alcohol misuse but occurring in individuals who consume little to no alcohol. This condition exists on a spectrum, with simple fatty liver (steatosis) being the mildest form and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) representing a more severe and progressive variant. NAFLD often goes unnoticed in its early stages, making it a “silent” condition with potentially serious consequences.
The Lifestyle-Liver Connection
Modern sedentary lifestyles and diets high in processed foods and added sugars have fostered an environment conducive to NAFLD development. The link between poor dietary choices, obesity, and insulin resistance is a pivotal factor. Diets rich in refined carbohydrates and sugary foods can lead to insulin resistance, causing the liver to store excess fat. This accumulation of fat can trigger inflammation and potentially progress to more severe forms of NAFLD.
Unveiling the Potential Dangers
While early-stage NAFLD may not elicit noticeable symptoms, its unchecked progression can lead to substantial health risks. NASH, characterized by fat accumulation, inflammation, and cell damage in the liver, poses a higher risk of complications. Prolonged inflammation and damage can culminate in fibrosis, where scar tissue forms in the liver. Advanced fibrosis can eventually result in cirrhosis, severely impairing liver function and raising the risk of liver cancer.
Strategies to Confront NAFLD
Addressing NAFLD requires proactive lifestyle changes:

Nourishing Diet:
Prioritize whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Minimize consumption of sugary foods, refined carbohydrates, and processed snacks.
Physical Activity:
Regular exercise helps manage weight, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce fat accumulation in the liver.

Moderate Alcohol Consumption:
While NAFLD is unrelated to alcohol, moderation is key. Excessive alcohol can exacerbate liver damage.
Holistic Health Management:
Liver Detox IV Treatment, enriched with crucial amino acids, offers a targeted approach to supporting liver function. These amino acids, key players in this treatment, aid in detoxification, energy production, and cellular regeneration. While lifestyle changes remain essential, Liver Detox Treatment provides a supplementary strategy to optimize liver health and navigate challenges like NAFLD. Collaborating with healthcare professionals can tailor this treatment to individual needs, ultimately promoting comprehensive wellness.


Professional Consultation:
Regular medical check-ups facilitate early NAFLD detection and intervention.
Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial. Even modest weight loss can significantly improve liver health.

Conclusion
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease serves as a stark reminder of the interplay between our lifestyles and health outcomes. As NAFLD’s prevalence rises, taking charge of our habits becomes paramount. By embracing a balanced diet, engaging in physical activity, and making informed choices, we can not only thwart the onset and progression of NAFLD but also enhance our overall well-being. NAFLD may be a silent health epidemic, but through awareness and action, we can turn the tide and ensure healthier lives for ourselves and future generations.

